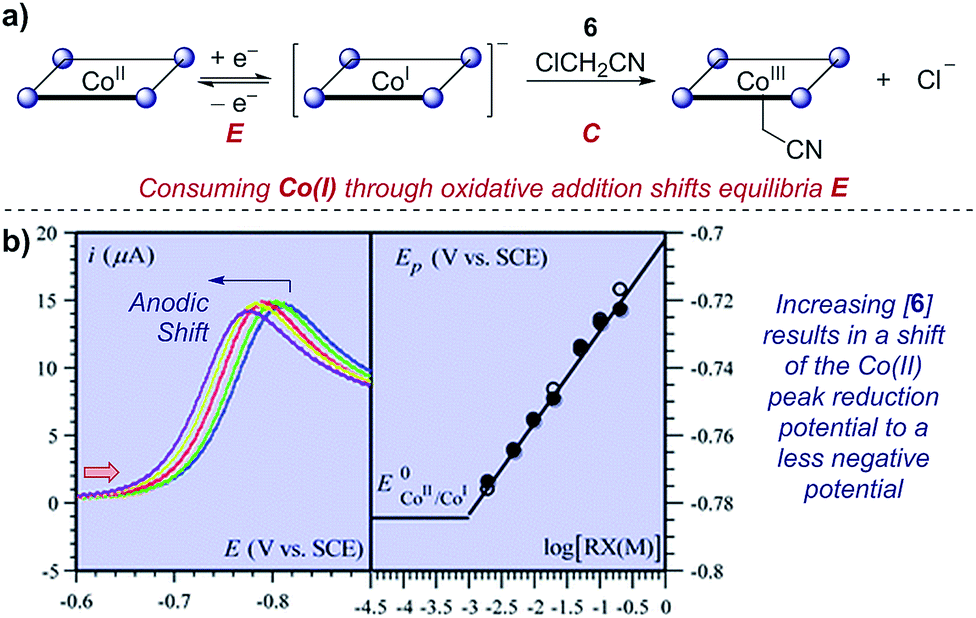
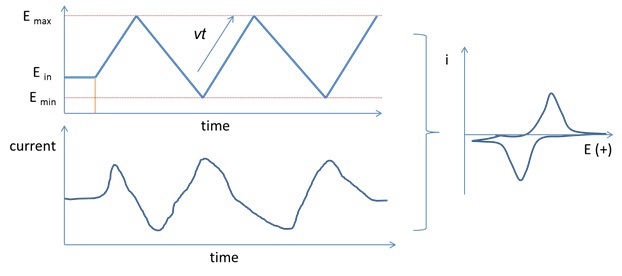
In a cyclic voltammetry experiment the working electrode potential is ramped linearly versus time. So according to the above equation and to keep the same charge value the current should be increased thats way the peak current is.
Electrochemistry Methods The Pan Research Group The
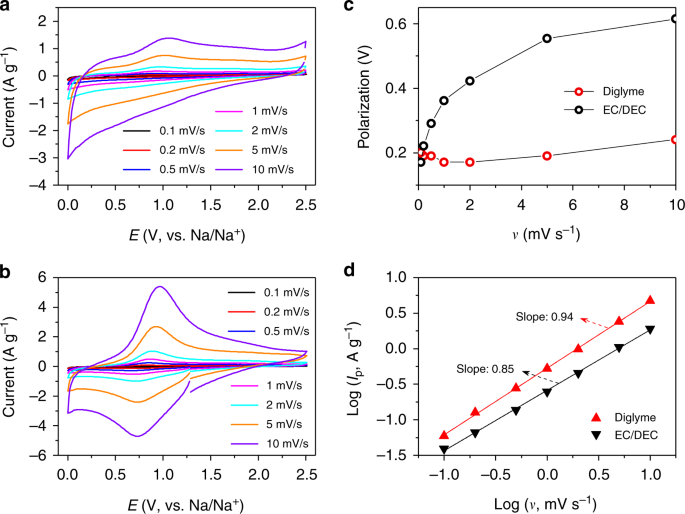
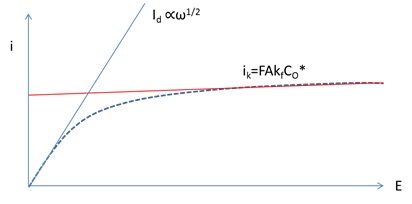
Cv scan rate dependence. The diffusion coefficient d for lithium ion intercalation into the wo 3 film. Rates are given by kredox z exp µ gredox kbt 16 if we plot a series of the free energy profiles as a function of voltage the free energy of r will be invariant with voltage whereas the right handside o e shows a strong dependence. If the kinetic parameter electron transfer rate k 0 is sufficiently fast for a reaction. When the scan rate is increased the time will be decreased. This highlights an important point when examining lsv and cyclic voltammograms although there is no time axis on the graph the voltage scan rate and therefore the time taken to record the voltammogram do strongly effect the behaviour seen. O ne r 2 and there is no homogenous reaction and surface adsorption of any reactant and product.
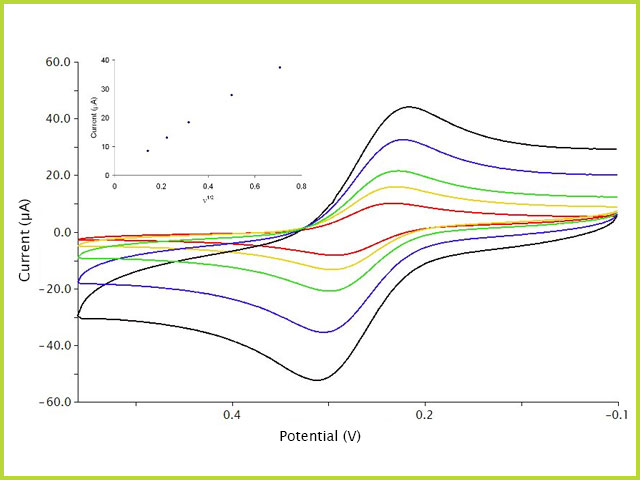
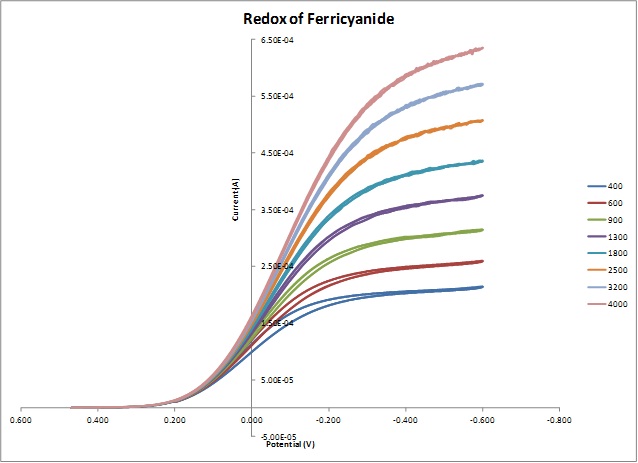
Scan rate dependence of cv and its peak current ip of a reversible reaction system. In order to assess the effect of the scan rate on the li ion diffusion coefficient as calculated from cyclic voltammetry cv a series of cv experiments at various rates namely 2 5 10 20 and 50 mvs has been carried out for the same wo 3 film prepared by electron gun deposition at room temperature. This is a distinct advantage of cyclic voltammetry over other voltammetric techniques. The expected characteristics of the cv were only obtained with a very slow scan rate of 2 mv s 1. Scan limits were 00 and 27 v. I have recorded the cvs at different scan rate 100 1000 mv and plotted the graphs for peak current vs square root of scan rate.
The capacitor was held at 00 v for 10 min between scans. Voltammograms were recorded at scan rates of 316 10 316 100 and 316 mvs. A second capacitor was used to show cvs scan rate dependence. As the current is proportional to the flux towards the electrode the magnitude of the current will be lower at slow scan rates and higher at high rates. Unlike in linear sweep voltammetry after the set potential is reached in a cv experiment the working electrodes potential is ramped in the opposite direction to return to the initial potential. In the case of polycrystalline electrodes the buffer capacity was kept close to the equilibrium state over the whole scan rate range.
However at the slower scan rate the peak on the reverse scan disappears. In contrast the electrochemical response of nanostructured electrodes was strongly dependent on the scan rate. Cyclic voltammetry cv is a type of potentiodynamic electrochemical measurement. At the faster scan rate we see two peaks. I have found it non linear. Cyclic voltammetry normalized by scan rate.
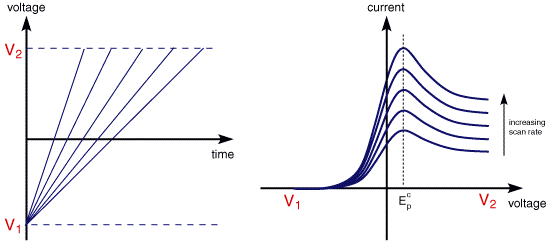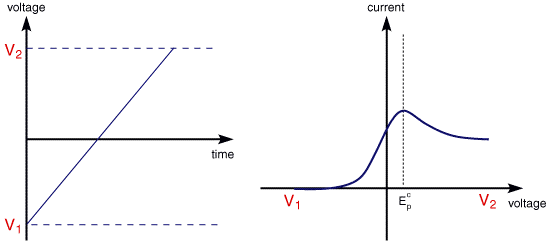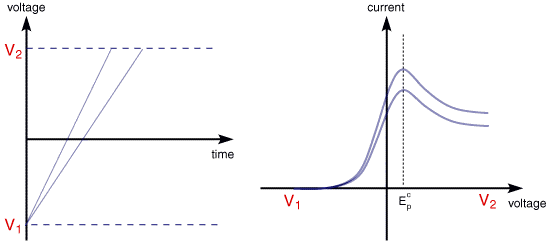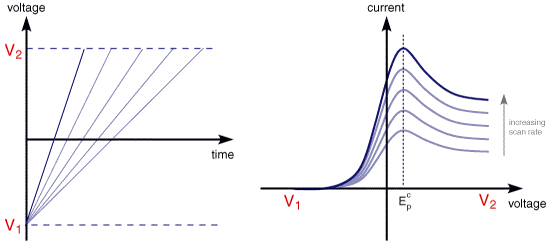
The illustration below for example shows the cyclic voltammogram for the same redox couple at both a faster a and a slower b scan rate.